Theme rooms on the 2nd floor
SKIN
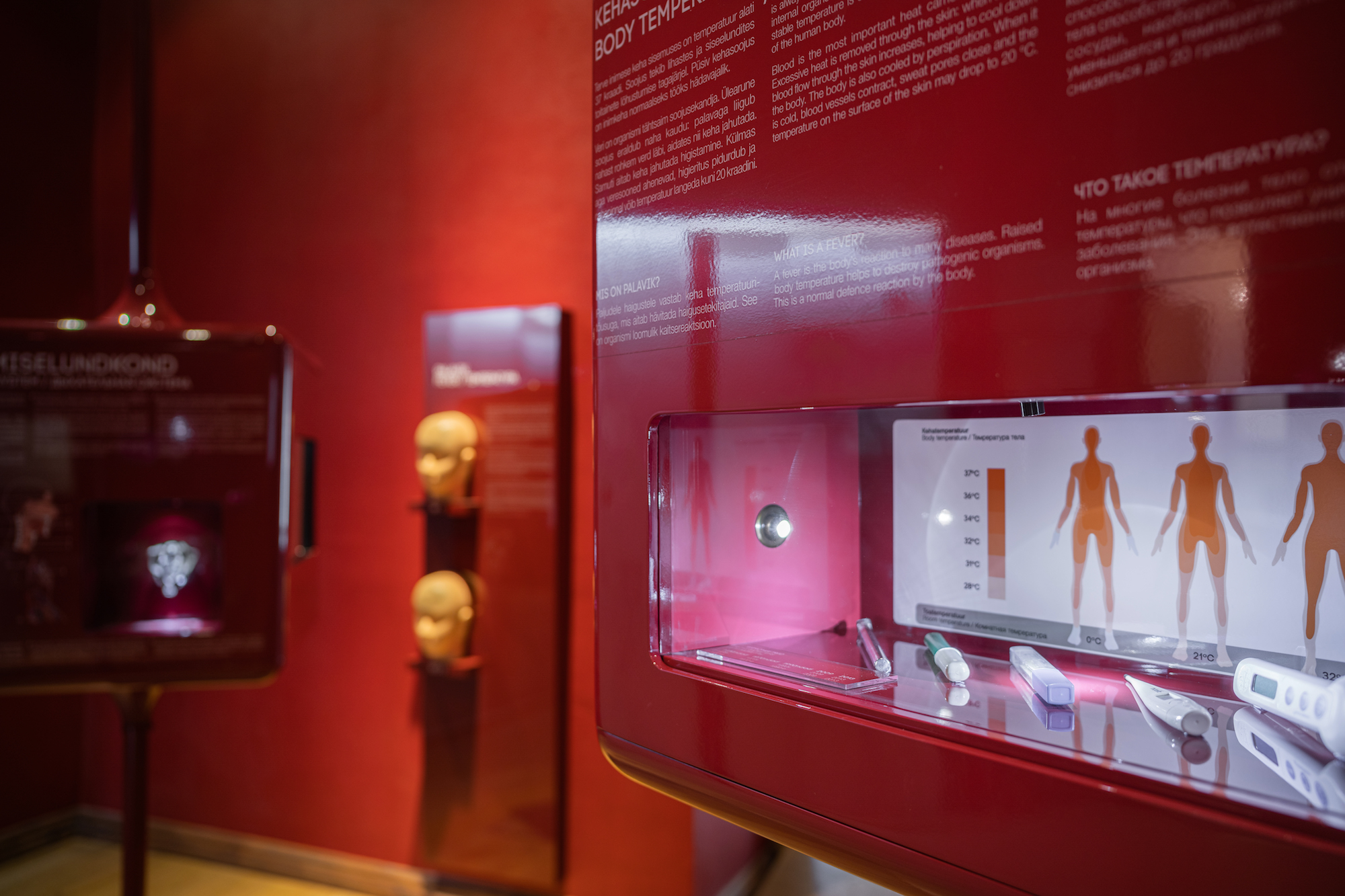
The area of human skin is approximately 2 m2. The function of the skin, together with hair and nails, is to protect and shield the body from injury and invasion of microbes. What is the skin composed of and why some people have curly hair while others have straight hair is explained in the section “Integumentary system”
THE SKELETON AND MUSCLES
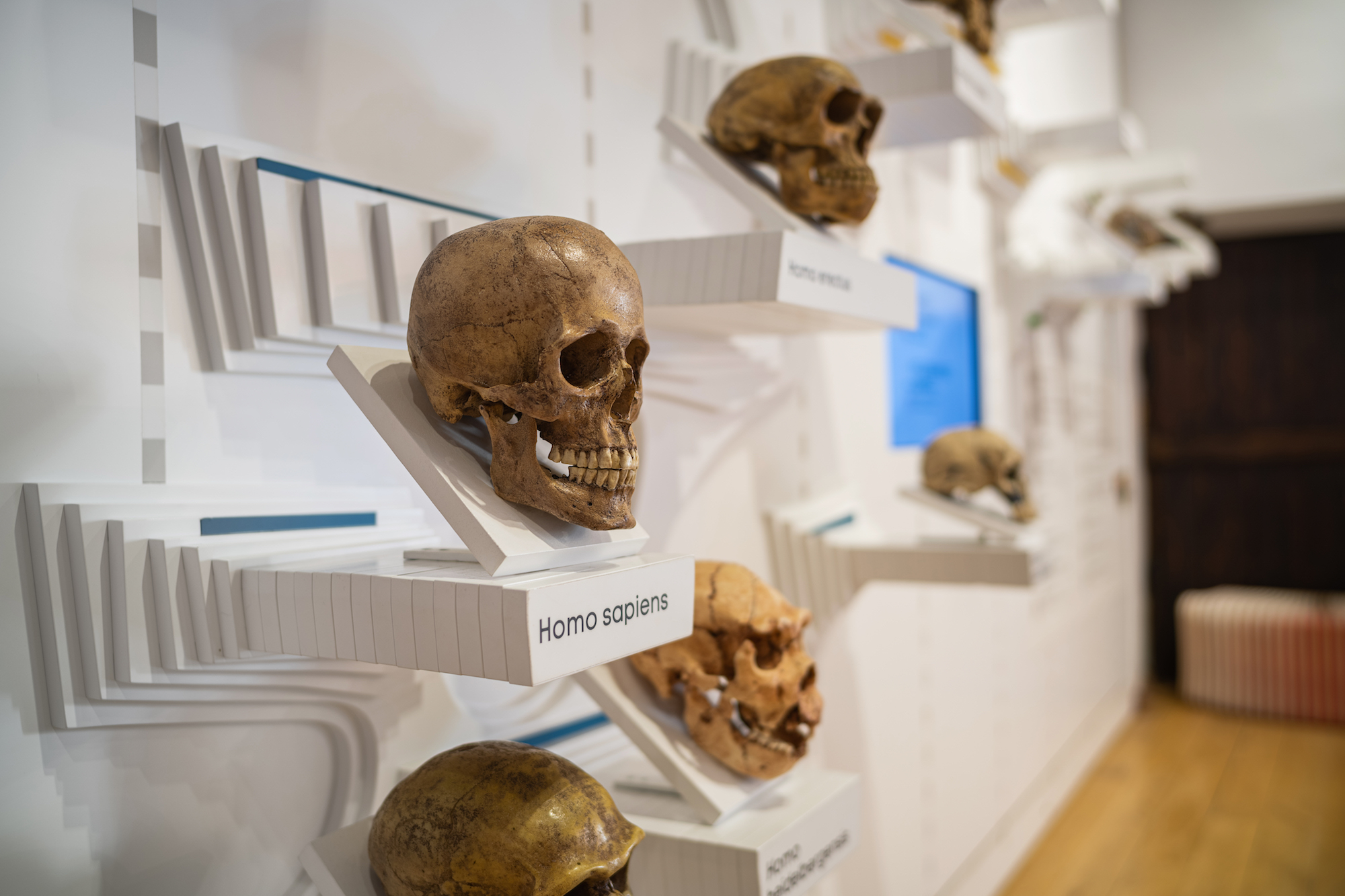
The skeleton gives the body its characteristic shape, protects internal organs and together with the muscles allows us to move. To see how a bone fracture heals, what parts does the skull include and what is a sarcomere, visit the bones/muscles box.
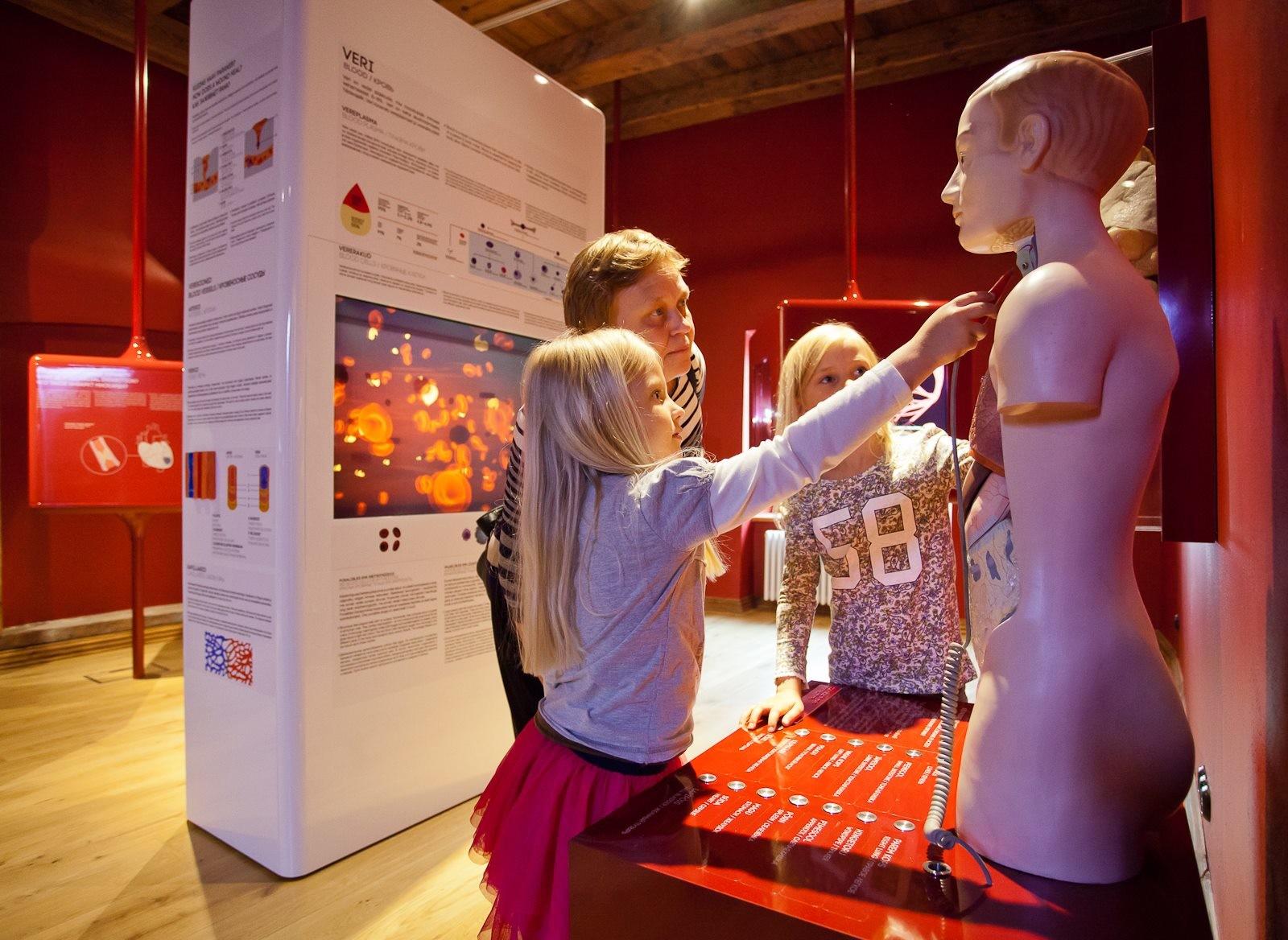
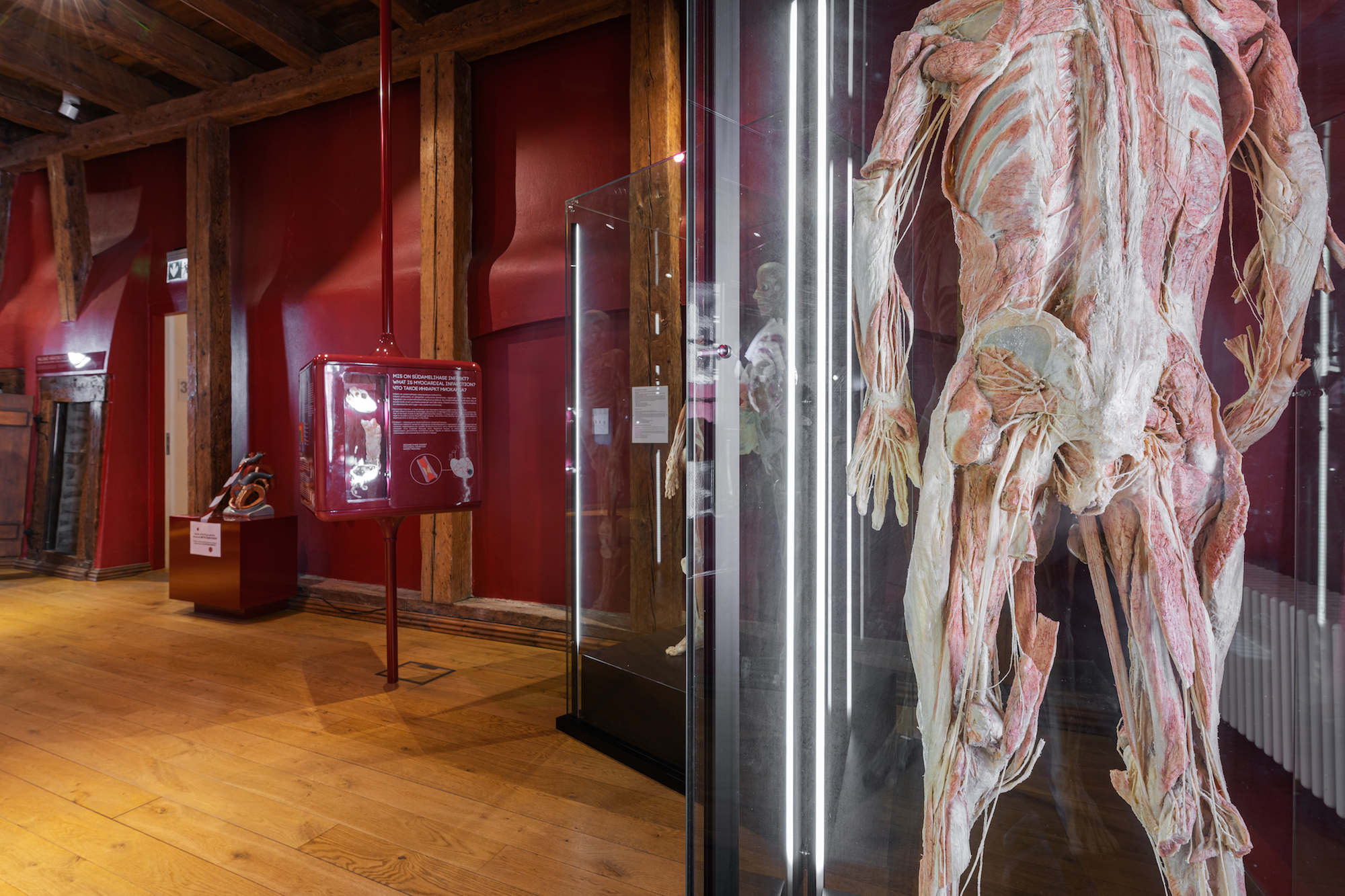
BLOOD CIRCULATION
Blood circulation connects all parts of the human body and reaches every single cell in our body. It takes less than a minute for a red blood cell to complete one circuit around your body. Blood is pumped around by the heart. The red Blood Room will give a detailed overview of the composition and functions of the heart and blood.
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
The lymphatic system is part of the circulatory system, comprising a network of lymphatic vessels and small structures called lymph nodes. The function of the lymphatic system is to collect lymph and fight diseases. The life-sized glass book shows the composition of a lymph node and the location of lymph nodes in our body.
ENDOCRINE GLANDS
Endocrine glands produce chemical substances – hormones – which together with the nervous system regulate the functioning of the human body. Various glands and the hormones they produce are introduced by the computer programme “Body chemistry”.
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
The immune system protects the body against intruders. Those who wish to know more can use the computer programme “Body defence. Fight against intruders.”
RESPIRATORY ORGANS
The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen and to remove carbon dioxide. What do different parts of the respiratory system look like and how vice is produced?
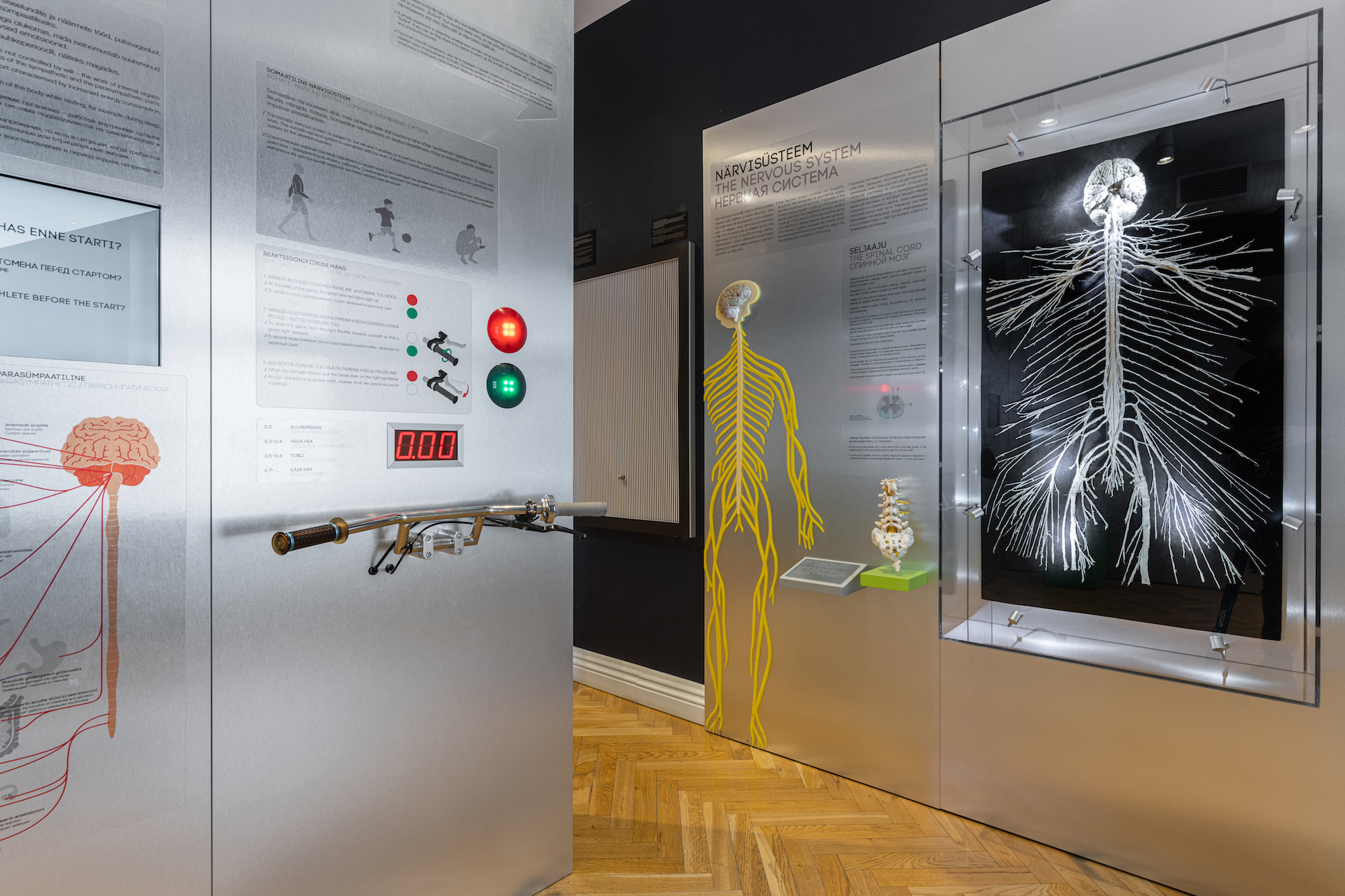
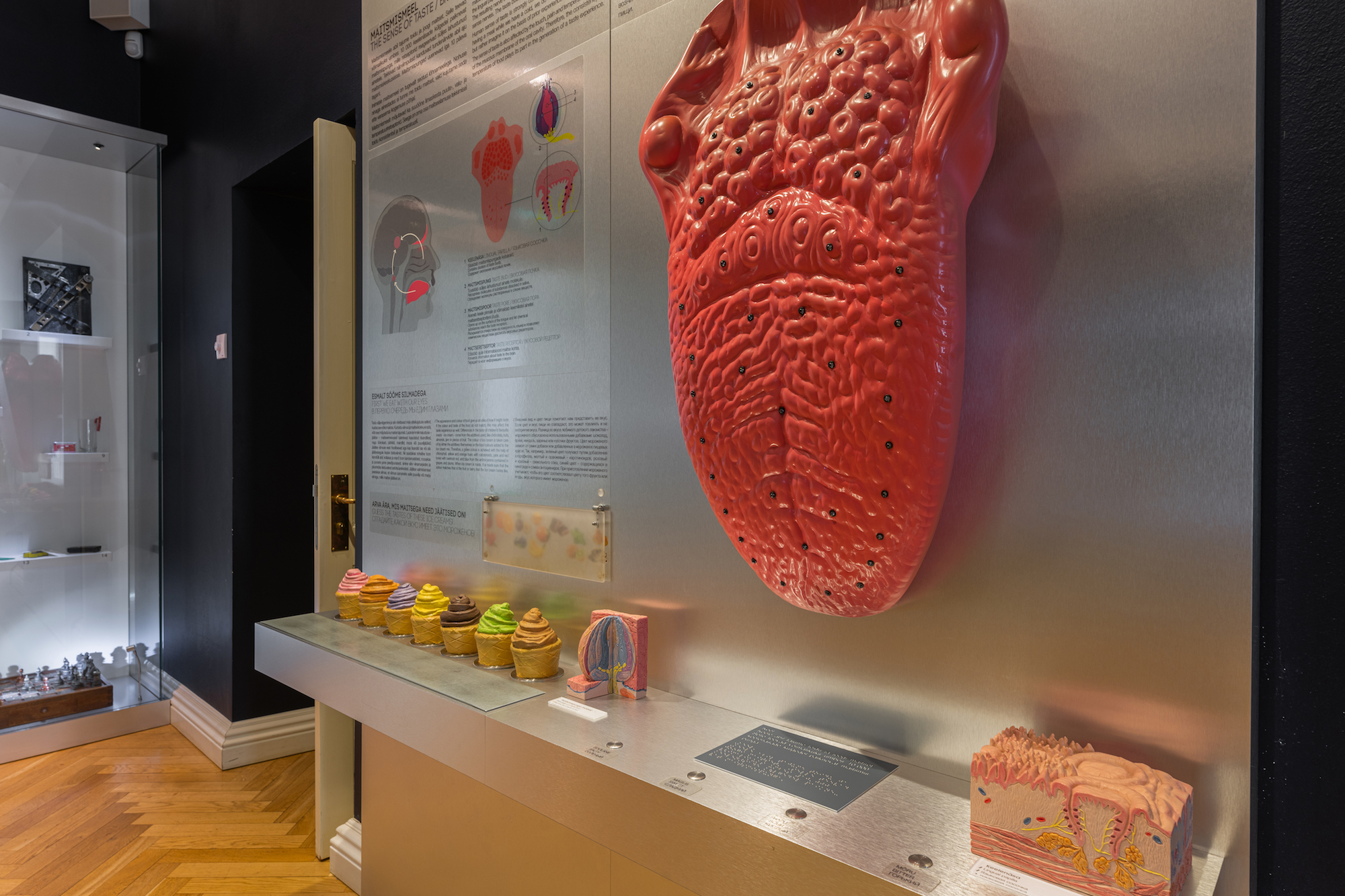
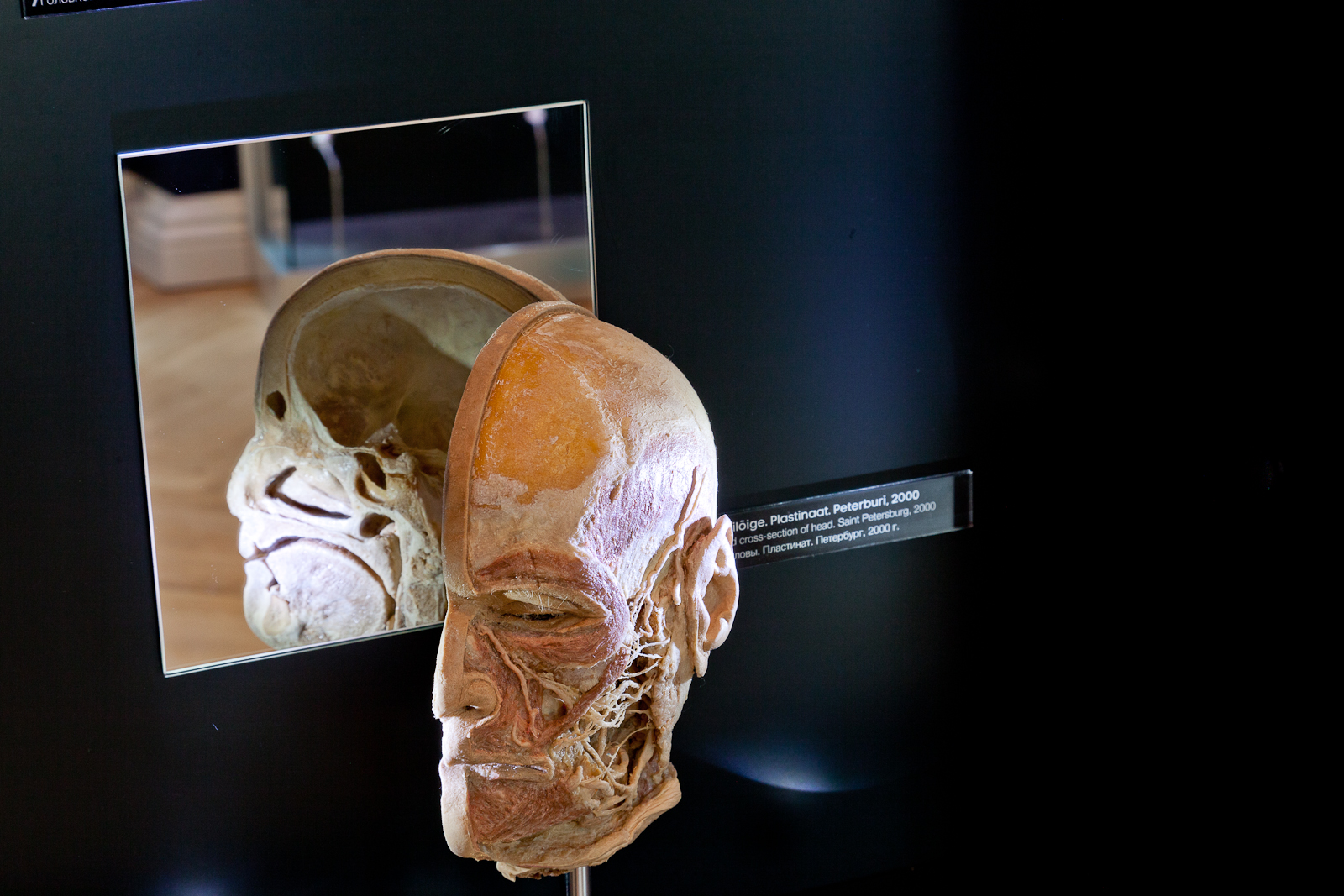
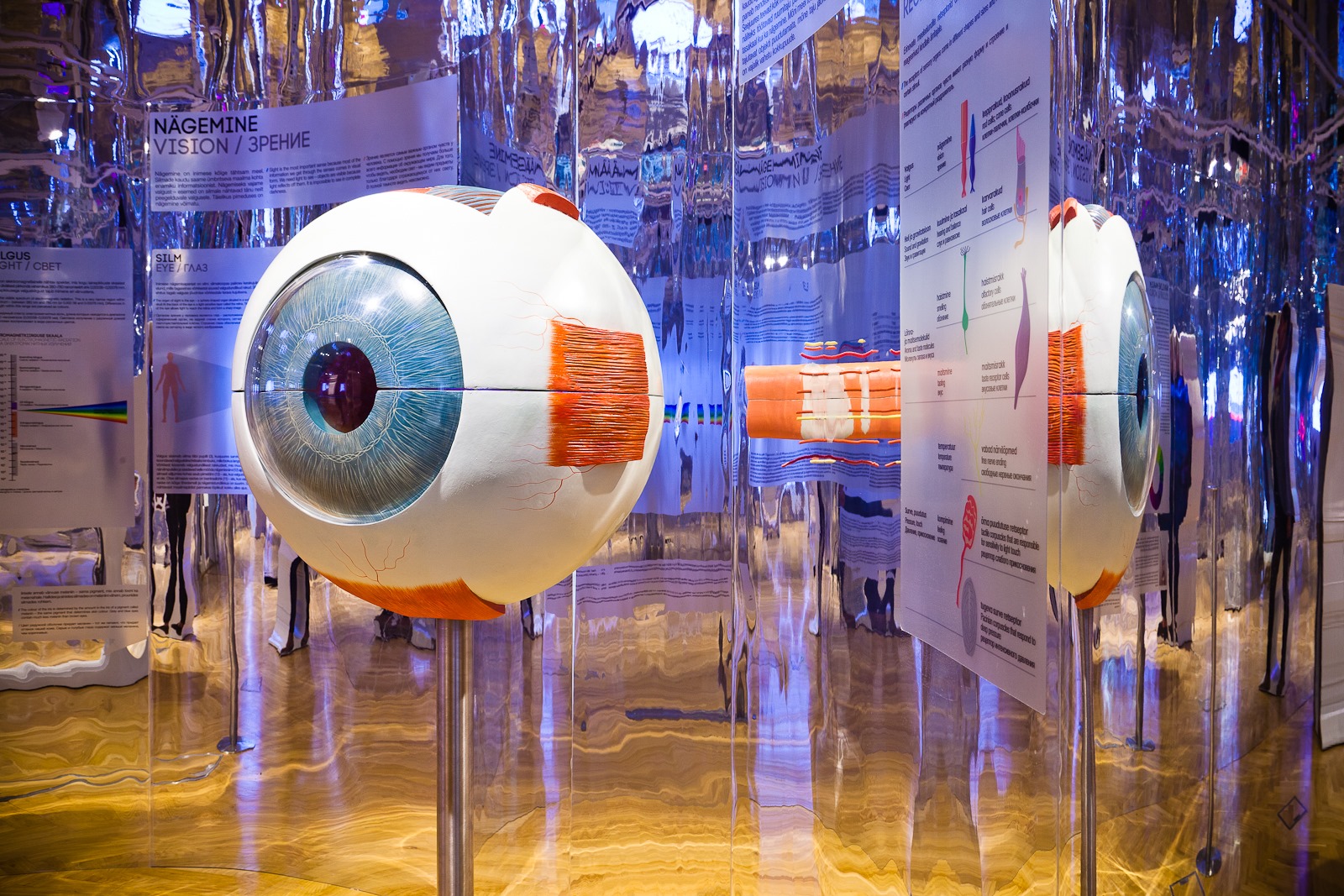
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM AND SENSES
Nerves enable different parts of the body to function as a whole. Nerves start from the brain or the spinal cord and reach all parts of the body, even teeth and bones. The section of nerves and senses describes the composition of the brain, the functions of the nervous system and sensory organs.
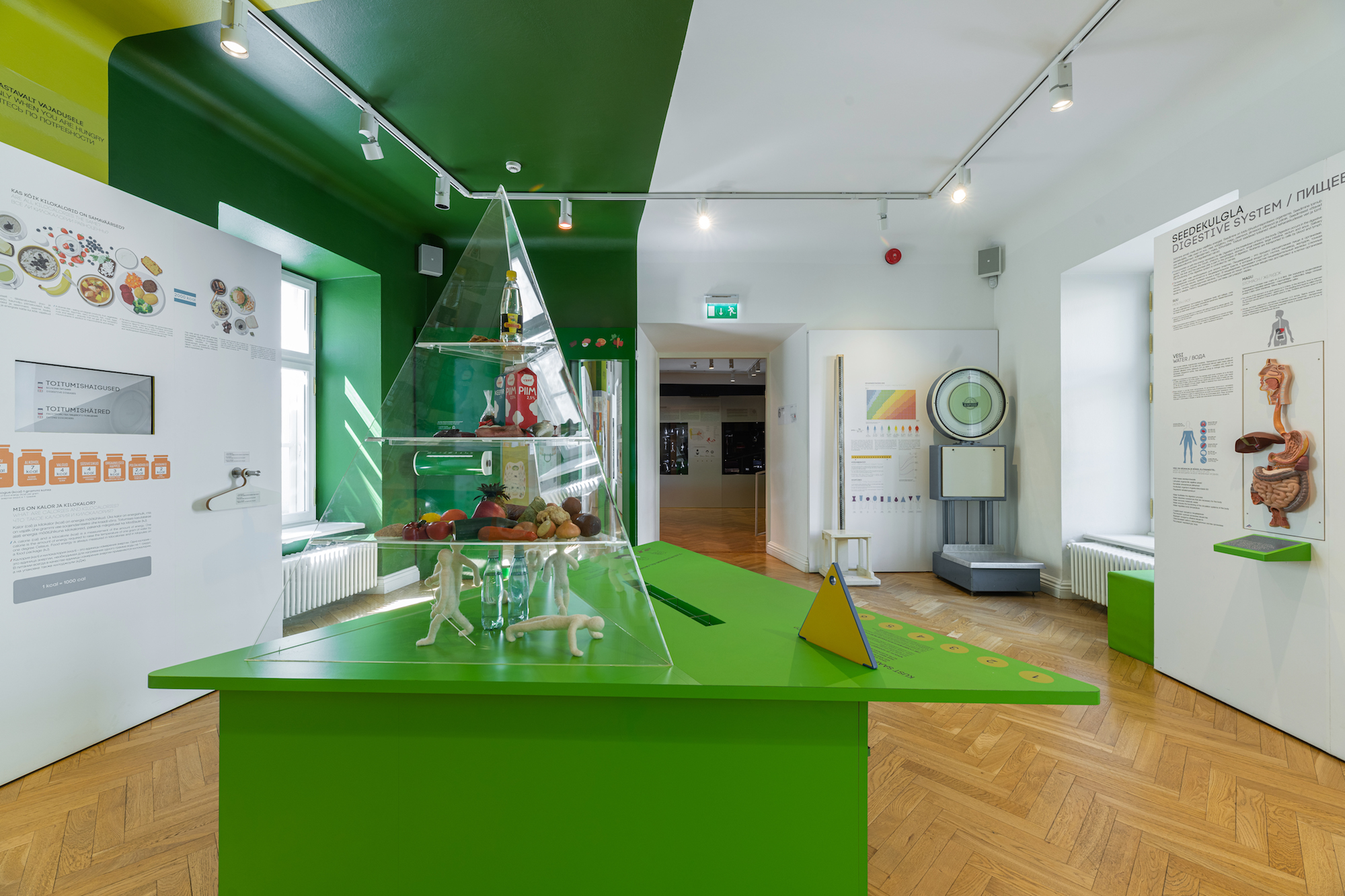
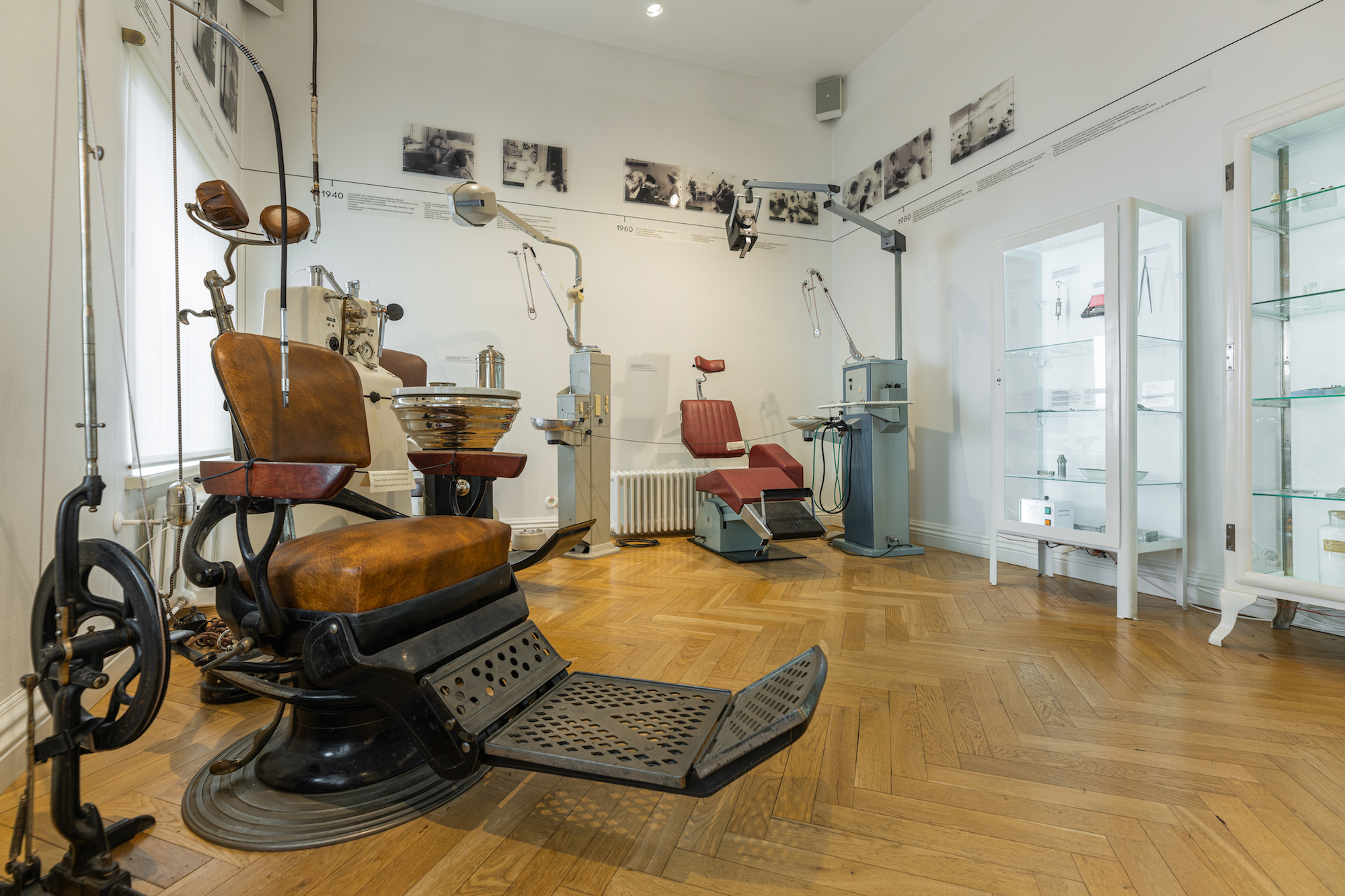
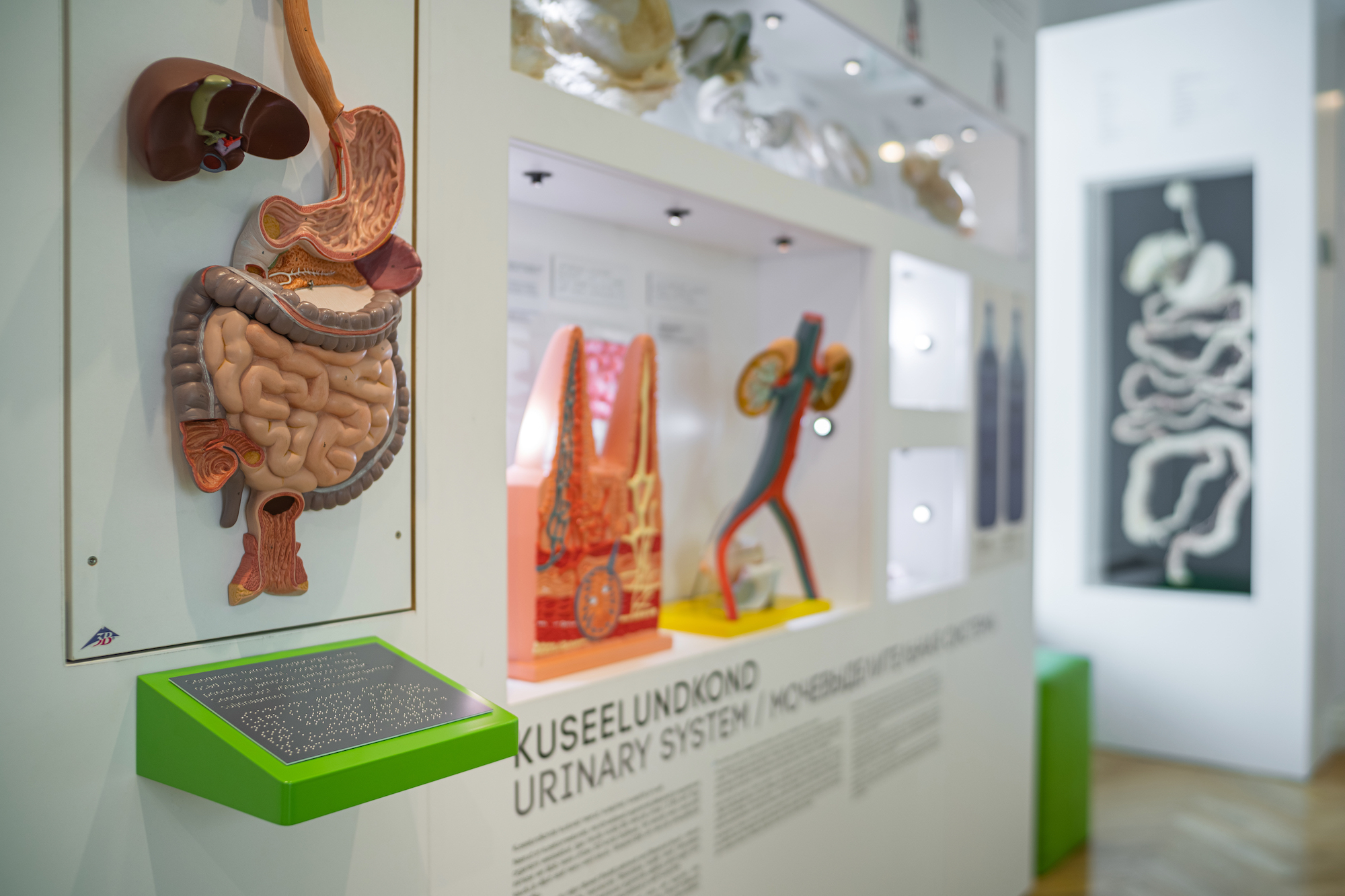
DIET. TEETH. DIGESTIVE AND EXCRETORY SYSTEMS
We eat to stay alive but also for pleasure. In the Diet Room we will explain what is a healthy diet and what causes eating disorders. The Teeth Room provides a historical overview of dentist chairs and instruments.
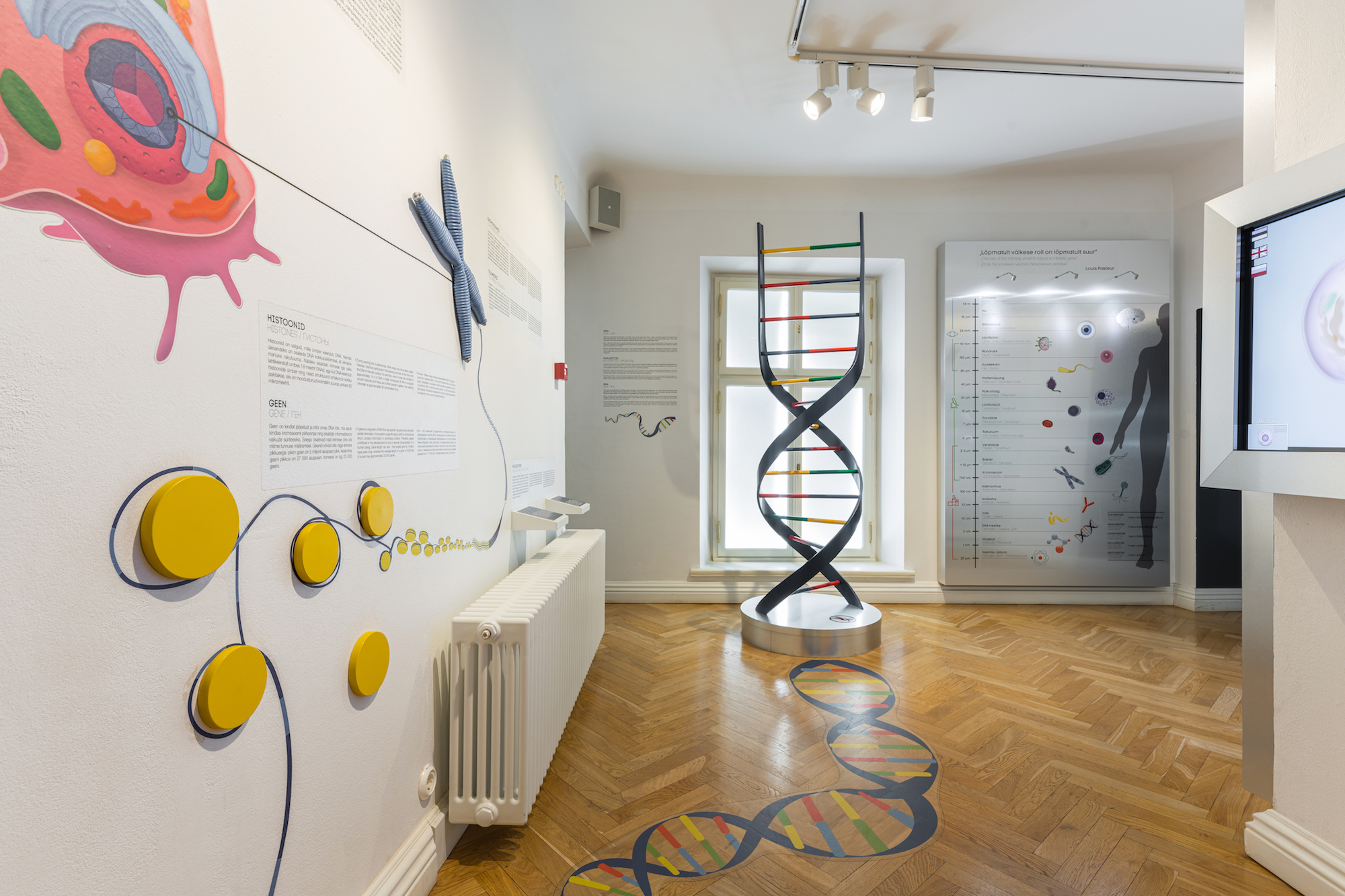
DNA AND 100 000 MAGNIFIED MODEL OF A CELL
The smallest unit of the human body is the cell. Cells come in different shapes and sizes and have different functions. The inside of a cell, different cell types and tissues are shown in the Cell Room. You can also listen to a 7-minute lecture about the composition of the cell.
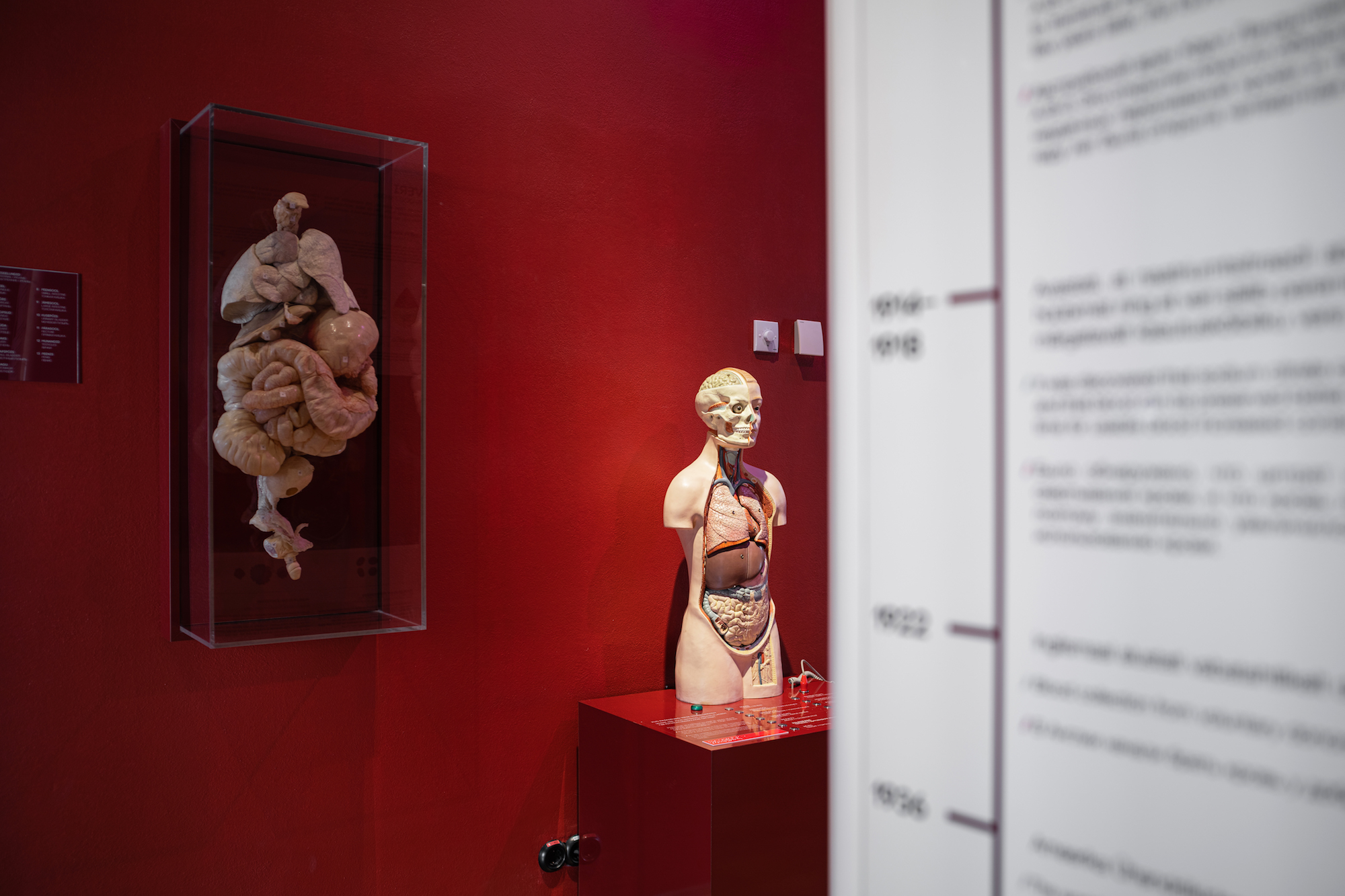
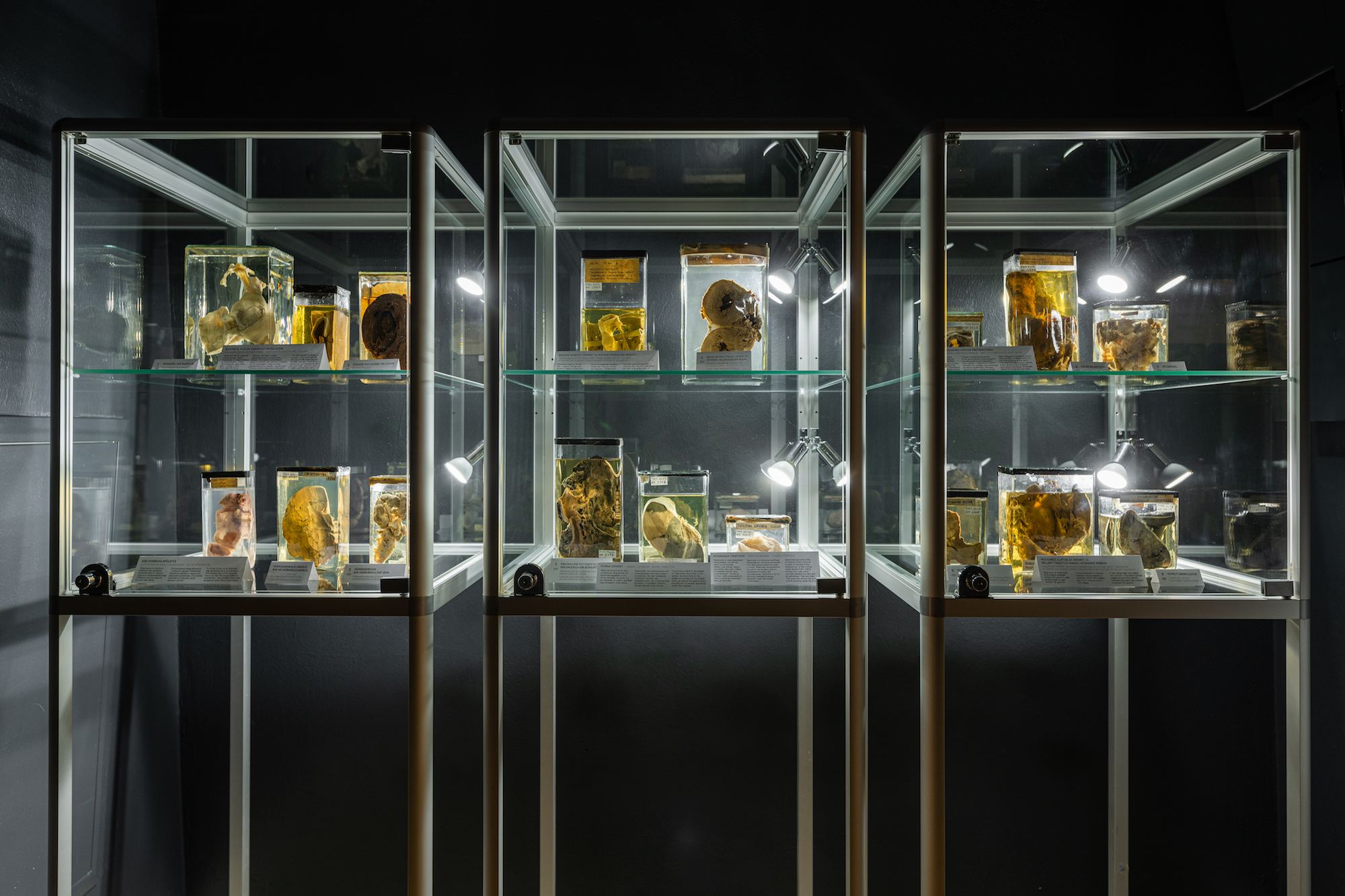
FLUID EMBALMED SPECIMENS
Historical fluid-embalmed specimens were donated to the collection of the Estonian
Health Care Museum in February 2020 by the East Tallinn Central Hospital Centre of
Pathology. The organs, which are
preserved in conservation fluid, demonstrate rare diseases and malformations. We are
exhibiting the specimens which visitors may find the most interesting.